About Us
What is MiOncoCirc?
MiOncoCirc is the first extensive clinical, cancer-centric resource of circRNAs. Most importantly, our database has been largely constructed from clinical cancer samples (2,000+) across a plethora of disease sites, while other resources have characterized circRNAs from cancer cell lines. The transcriptional processes, and resulting circRNA formation, that occur in a dish versus a native tumor microenvironment will undoubtedly be vastly different, making MiOncoCirc a better representation of the true circRNA profile associated with cancer. Furthermore, MiOncoCirc represents a rich resource containing circRNAs from primary tumors, metastases, and very rare cancer types. Researchers who are interested can also query mutations and copy-number since MiOncoCirc samples are collected from previously published genomic papers (Mody et al., 2015, Robinson et al., 2015, and Robinson et al., 2017).
Our Bioinformatics Pipeline
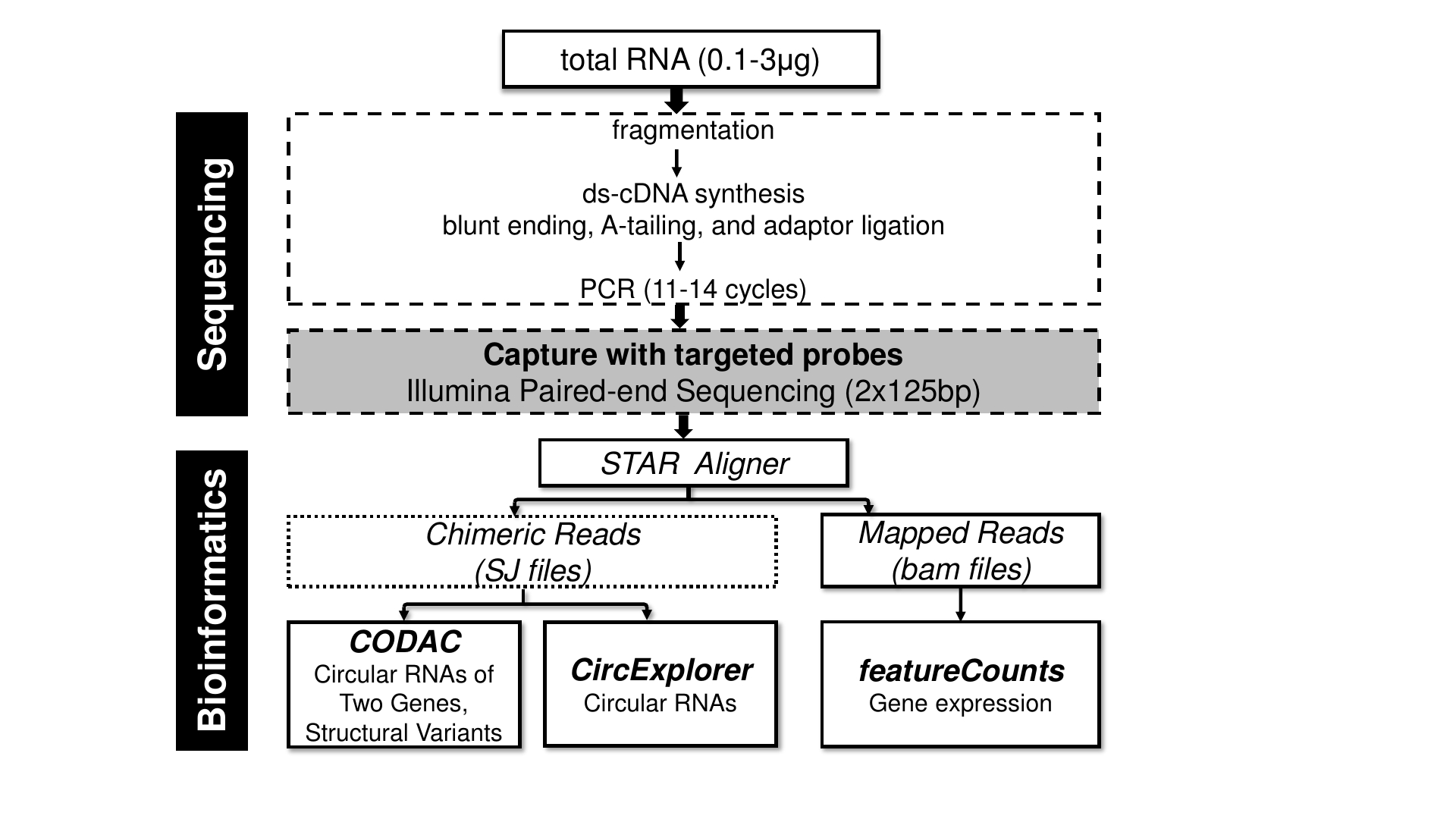
The transcriptome for each sample was profiled by paired-end, strand specific capture RNA-seq with moderate depth (~50M-60M). To detect backspliced (circular) reads from RNA-seq libraries, we used the pipeline CIRCexplorer (Zhang et al., 2014). CIRCexplorer has been shown to achieve high sensitivity and specificity among current circRNA bioinformatics tools. In addition, we employed the pipeline CODAC to discover a new class of circRNAs, read-through circRNAs (rt-circRNA). CODAC was initially developed to call structural rearrangements in paired-end RNA-seq but has been recently extended to the annotation of circRNAs, especially those that involve more than one gene.
Browsing the circRNAs
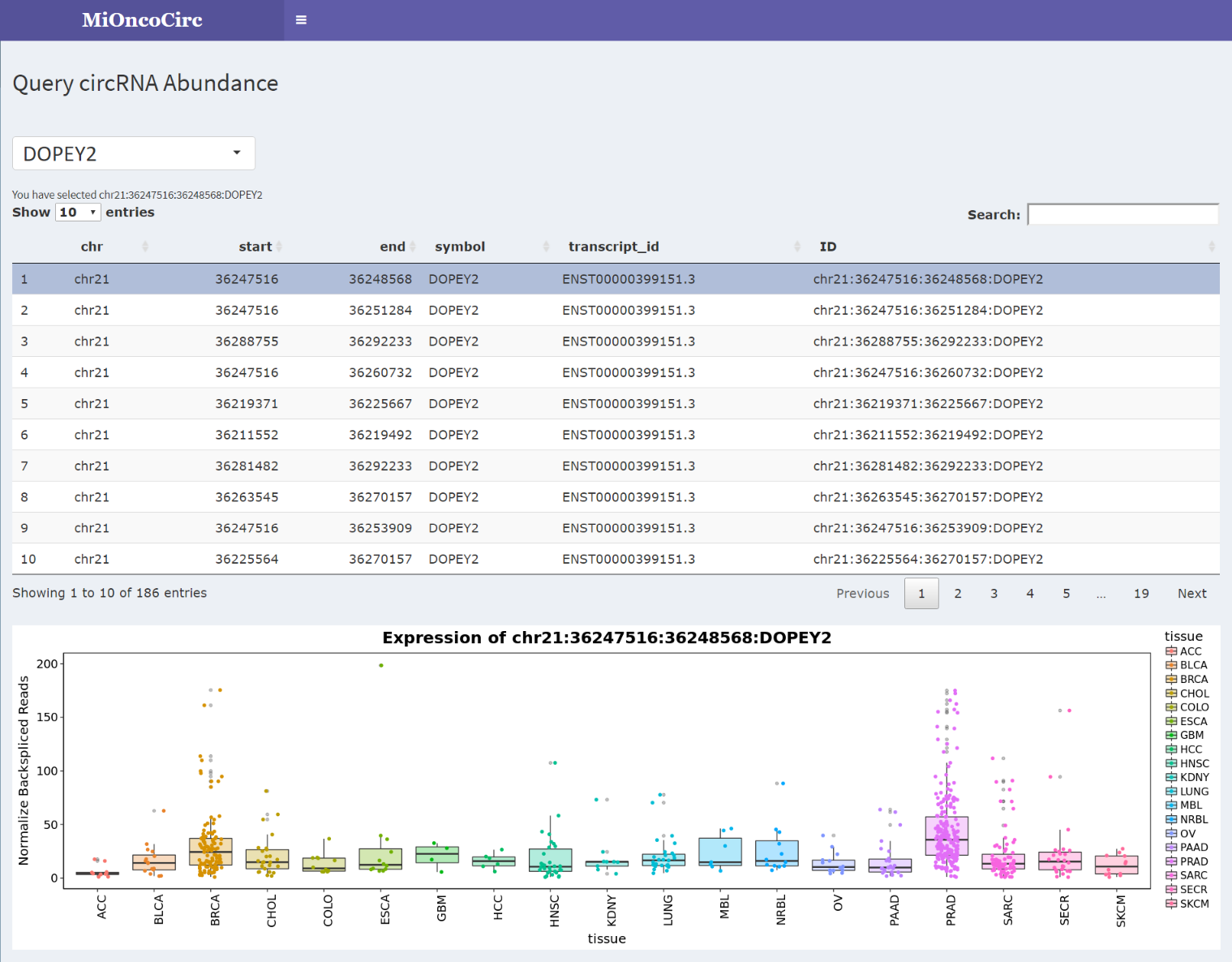
Using our "Query Data" page, the users can browse all circRNAs of any chosen gene. Furthermore, by clicking on the circular isoform on the displayed table, the users can see its abundance across different cancer lineages.
Reference
Mody, R., Wu, Y., Lonigro, R., Cao, X., Roychowdhury, S., Vats, P., Frank, K., Prensner, J., Asangani, I., and Palanisamy, N. et al. (2015). Integrative Clinical Sequencing in the Management of Refractory or Relapsed Cancer in Youth. JAMA 314, 913.
Robinson, D., Van Allen, E., Wu, Y., Schultz, N., Lonigro, R., Mosquera, J., Montgomery, B., Taplin, M., Pritchard, C., and Attard, G. et al. (2015). Integrative Clinical Genomics of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 161, 1215-1228.
Robinson, D., Wu, Y., Lonigro, R., Vats, P., Cobain, E., Everett, J., Cao, X., Rabban, E., Kumar-Sinha, C., and Raymond, V. et al. (2017). Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature 548, 297-303.
Zhang, X., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Lu, X., Chen, L., and Yang, L. (2014). Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization. Cell 159, 134-147.